Allyl And Vinyl Structure

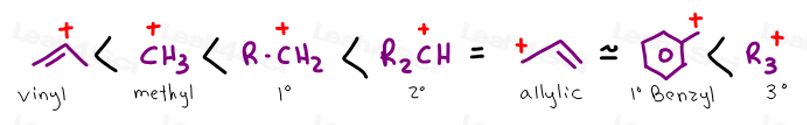
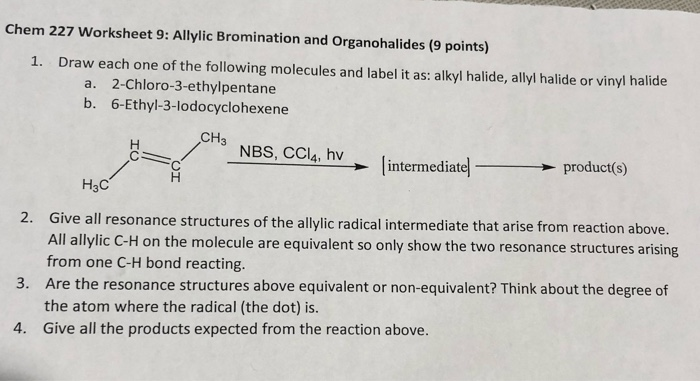
On a carbon skeleton sp 2 hybridized carbons or positions are often called vinylic.
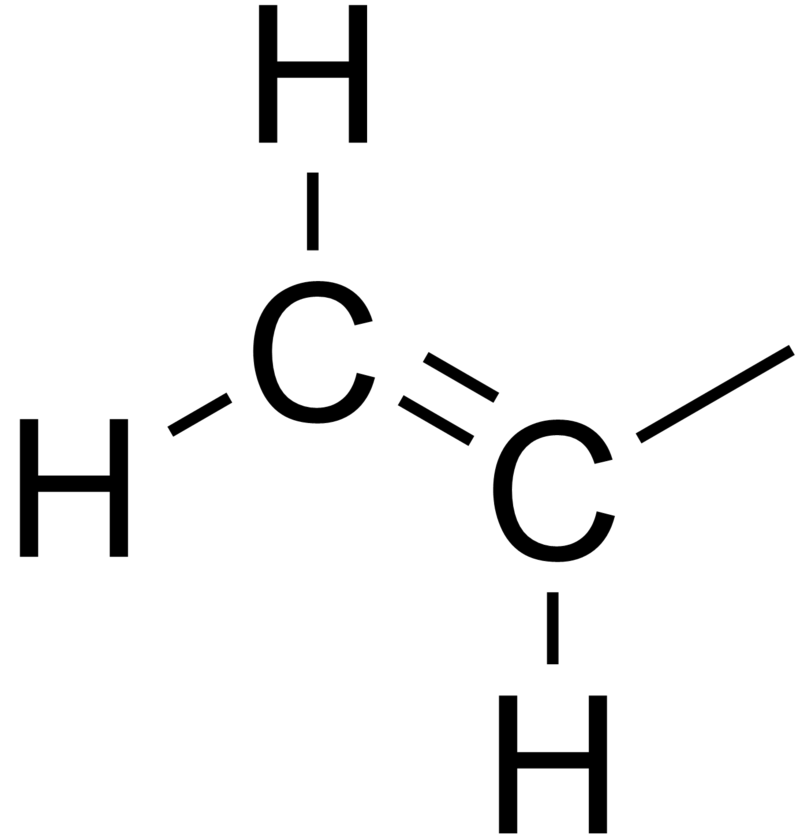
Allyl and vinyl structure. Allyl vinyl ether c5h8o cid 221523 structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities. The name is derived from the latin word for garlic allium sativum. The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group.
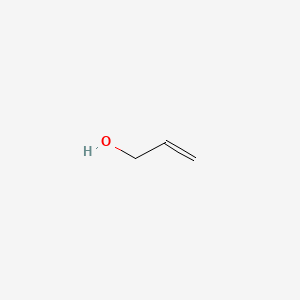
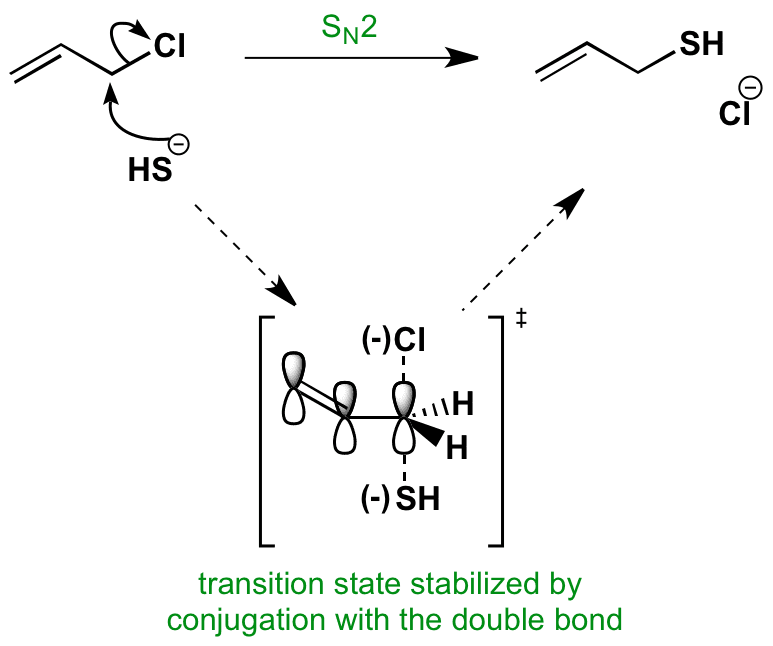
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds. A styrenic crosslinker with two vinyl groups is called divinyl benzene. Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms on the other hand vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms. An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h2c ch ch2r where r is the rest of the molecule.
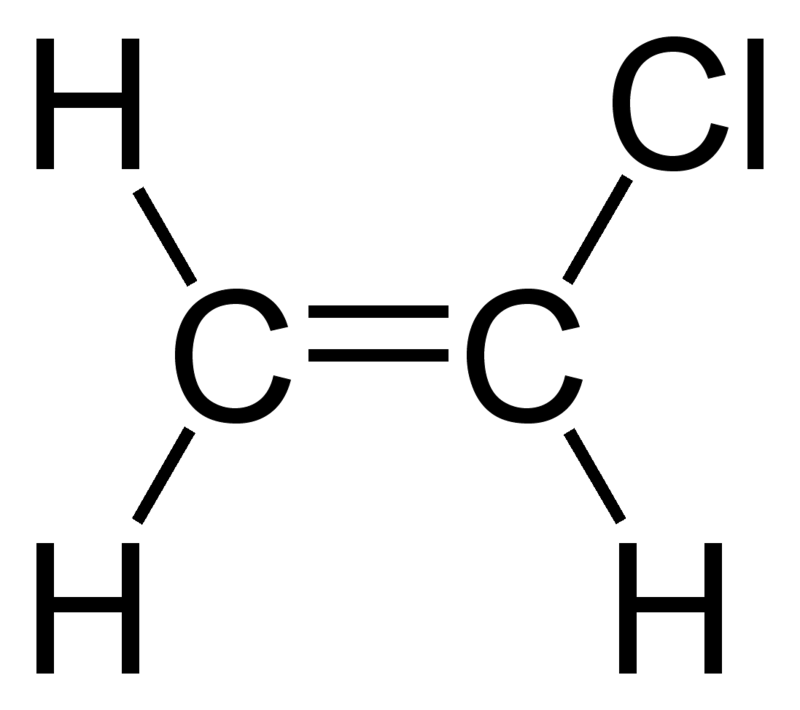
Furthermore the allyl chloride occurs as a liquid while vinyl chloride is a colourless gas at room temperature. The term allyl applies to many compounds related to h2c ch ch2 some of which are of practical or of everyday importance for example allyl chloride. Allyls acrylates and styrenics contain vinyl groups. The key difference between allyl chloride and vinyl chloride is that ally chloride contains its chlorine atom bonded to the carbon atom that is adjacent to the double bond whereas vinyl chloride contains its chlorine atom bonded to one of the two carbon atoms in the double bond.
In 1844 theodor wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it schwefelallyl.